Figure 1
Download original image
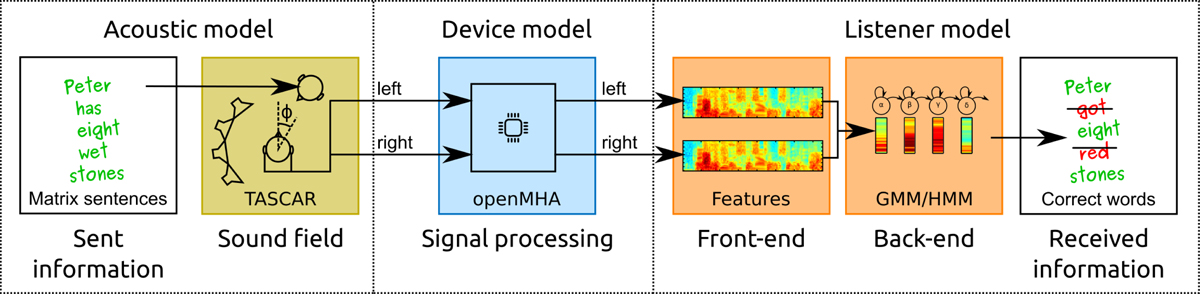
Overview of the employed combination of existing model components to create a toolchain for predicting the human speech recognition performance in complex (that is, challenging) acoustic listening conditions. Speech information is presented in a simulated sound field, the acoustic signals are rendered to the ear level and optionally processed with a hearing device model before they are recognized by a re-purposed automatic speech recognition system. In the first square, speech information is encoded by selecting a matrix sentence. The sentence is presented in a virtual acoustic scene created with the software TASCAR. The output of that step, a noisy binaural speech recording, is optionally processed with a hearing aid model, implemented with the software openMHA. The (optionally processed) noisy recording is recognized with an ASR system trained to recognize matrix sentences (orange squares), where a hearing loss can be configured in the feature extraction stage. In the last square, the percentage of correctly recognized words is evaluated. The approach is described in detail in the Section 2.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


