Open Access
| Issue |
Acta Acust.
Volume 9, 2025
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Article Number | 33 | |
| Number of page(s) | 16 | |
| Section | Virtual Acoustics | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/aacus/2025018 | |
| Published online | 03 June 2025 | |
- F. Jacobsen: A note on instantaneous and time-averaged active and reactive sound intensity. Journal of Sound and Vibration 147 (1991) 489–496. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-460X(91)90496-7 [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- H. Kuttruff: Room acoustics, 6th edn. CRC Press, Boca Raton, 2017. https://doi.org/10.1201/9781315372150 [Google Scholar]
- J.-D. Polack: Playing billiards in the concert hall: the mathematical foundations of geometrical room acoustics. Applied Acoustics 38 (1993) 235–244. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-682X(93)90054-A [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- R. Badeau: Statistical wave field theory. Journal of the Acoustical Society of America 156 (2024) 573–599. https://doi.org/10.1121/10.0027914 [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- M. Nolan, E. Fernandez-Grande, J. Brunskog, C.-H. Jeong: A wavenumber approach to quantifying the isotropy of the sound field in reverberant spaces. Journal of the Acoustical Society of America 143 (2018) 2514–2526. https://doi.org/10.1121/1.5032194 [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- M. Berzborn, M. Vorländer: Directional sound field decay analysis in performance spaces. Building Acoustics 28 (2021) 249–263. https://doi.org/10.1177/1351010X20984622 [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- G. Götz, S. J. Schlecht, V. Pulkki: Common-slope modeling of late reverberation. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing 31 (2023) 3945–3957. https://doi.org/10.1109/TASLP.2023.3317572 [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- B. Alary, A. Politis, S. J. Schlecht, V. Välimäki: Directional feedback delay network. Journal of the Audio Engineering Society 67 (2019) 752–762. Available: https://doi.org/10.17743/jaes.2019.0026 [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- S. Bilbao, B. Alary: Directional reverberation time and the image source method for rectangular parallelepipedal rooms. Journal of the Acoustical Society of America 155 (2024) 1343–1352. https://doi.org/10.1121/10.0024975 [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- C.V. Hoorickx, E.P. Reynders: Numerical realization of diffuse sound pressure fields using prolate spheroidal wave functions. Journal of the Acoustical Society of America 151 (2022) 1710–1721. https://doi.org/10.1121/10.0009764 [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O. Robin, A. Berry, O. Doutres, N. Atalla: Measurement of the absorption coefficient of sound absorbing materials under a synthesized diffuse acoustic field. Journal of the Acoustical Society of America 136 (2014) EL13–EL19. https://doi.org/10.1121/1.4881321 [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- S. Dupont, M. Sanalatii, M. Melon, O. Robin, A. Berry, J.-C. Le Roux: Measurement of the diffuse field sound absorption using a sound field synthesis method. Acta Acustica 7 (2023) 26. https://doi.org/10.1051/aacus/2023021 [CrossRef] [EDP Sciences] [Google Scholar]
- E. Habets, S. Gannot: Generating sensor signals in isotropic noise fields. Journal of the Acoustical Society of America 122 (2007) 3464–3470. https://doi.org/10.1121/1.2799929 [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- M. Kustner: Spatial correlation and coherence in reverberant acoustic fields: extension to microphones with arbitrary first-order directivity. Journal of the Acoustical Society of America 123 (2008) 152–164. https://doi.org/10.1121/1.2812592 [Google Scholar]
- N. Akbar, G. Dickins, M.R.P. Thomas, P. Samarasinghe, T. Abhayapala: A novel method for obtaining diffuse field measurements for microphone calibration, in: IEEE ICASSP, Barcelona, Spain, 4–8 May, IEEE, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICASSP40776.2020.9054728 [Google Scholar]
- G. Theile: Comparison of two dummy head systems with due regard to different fields of application, in DAGA, Darmstadt, 84a0223.pdf, 1984. Available at https://pub.dega-akustik.de/DAGA_1982-1990.zip [Google Scholar]
- T. McKenzie, D.T. Murphy, G. Kearney: Diffuse-field equalisation of binaural ambisonic rendering. Applied Science 8 (2018) 1956. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8101956 [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- C. Armstrong, L. Thresh, D. Murphy, G. Kearney: A perceptual evaluation of individual and non-individual HRTFs: a case study of the SADIE II database. Applied Science 8 (2018) 2029. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8112029 [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- D.J. Moreau, J. Ghan, B. Cazzolato, A. Zander: Active noise control in a pure tone diffuse sound field using virtual sensing. Journal of the Acoustical Society of America 125 (2009) 3742–3755. https://doi.org/10.1121/1.3123404 [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- F. Holzmüller, A. Sontacchi: Frequency limitation for optimized perception of local active noise control, in DAGA, Hamburg, 6–9, March. 2023. Available at https://pub.dega-akustik.de/DAGA_2023/data/articles/000531.pdf [Google Scholar]
- S.J. Elliott, P. Joseph, A. Bullmore, P.A. Nelson: Active cancellation at a point in a pure tone diffuse sound field. Journal of Sound and Vibration 120 (1988) 183–189. https://doi.org/10.1006/jsvi.1996.0742 [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- K. Hiyama, S. Komiyama, K. Hamasaki: The minimum number of loudspeakers and its arrangement for reproducing the spatial impression of diffuse sound field, in 113th AES Conv, Los Angeles, USA, 5–8 October, 2002. Available at http://www.aes.org/e-lib/browse.cfm?elib=11272 [Google Scholar]
- A. Walther, C. Faller: Assessing diffuse sound field reproduction capabilities of multichannel playback systems, in 130th AES Convention, London, UK, 13–16, May 2011. Available at http://www.aes.org/e-lib/browse.cfm?elib=15895 [Google Scholar]
- M.P. Cousins, F.M. Fazi, S. Bleeck, F. Melchior: Subjective diffuseness in layer-based loudspeaker systems with height, in 139th AES Convention, New York, USA, October 29–November 1, 2015. Available at http://www.aes.org/e-lib/browse.cfm?elib=17983 [Google Scholar]
- S. Riedel, F. Zotter: Surrounding line sources optimally reproduce diffuse envelopment at off-center listening positions. Journal of the Acoustical Society of America 2 (2022) 094404. https://doi.org/10.1121/10.0014 168 [Google Scholar]
- S. Riedel, M. Frank, F. Zotter: The effect of temporal and directional density on listener envelopment. Journal of the Audio Engineering Society 71 (2023) 455–467. Available: https://doi.org/10.17743/jaes.2022.0088 [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- M. Blochberger, F. Zotter, M. Frank: Sweet area size for the envelopment of a recursive and a non-recursive diffuseness rendering approach, in 5th International Conference on Spatial Audio, 26–28 September, Ilmenau, Germany, Verband Deutscher Tonmeister e.V., 2019, pp. 151–157. https://doi.org/10.22032/dbt.39969 [Google Scholar]
- P. Heidegger, B. Brands, L. Langgartner, M. Frank: Sweet area using ambisonics with simulated line arrays, in DAGA, Vienna, Austria, 15–18 August, 2021. Available at https://pub.dega-akustik.de/DAGA_2021/data/articles/000374.pdf [Google Scholar]
- S. Riedel, L. Gölles, M. Frank, F. Zotter: Modeling the listening area of envelopment. in DAGA, Hamburg, Germany, 6–9 March, 2023. Available at https://pub.dega-akustik.de/DAGA_2023/data/articles/000289.pdf [Google Scholar]
- S. Riedel, M. Frank, F. Zotter, R. Sazdov: A study on loudspeaker SPL decays for envelopment and engulfment across an extended audience, in AES 2024 International Acoustics & Sound Reinforcement Conference, Le Mans, France, 23–26 January, 2024. Available at http://www.aes.org/e-lib/browse.cfm?elib=22368 [Google Scholar]
- T. Tanaka, M. Otani: An isotropic sound field model composed of a finite number of plane waves. Acoustical Science and Technology 44 (2023) 4. https://doi.org/10.1250/ast.44.317 [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- T. Tanaka, M. Otani: Spatially characterized pseudo-perfect diffuseness via finite-degree spherical harmonic diffuseness. JASA Express Letters 4 (2024) 071601. https://doi.org/10.1121/10.0026466 [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- T. Tanaka, M. Otani: Directionally characterized pseudo-perfect diffuseness: a detailed comparison of its theoretical formulations. Acoustical Science and Technology 45 (2024) 260–269. https://doi.org/10.1250/ ast.e24.16 [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- F. Zotter, S. Riedel, L. Gölles, M. Frank: Diffuse sound field synthesis: idela source layers. Acta Acustica 34 (2024) 16. https://doi.org/10.1051/aacus/2024023 [Google Scholar]
- I. Newton: The mathematical principles of natural philosophy, B. Motte, 1729, tranlation by Andrew Motte. Available at https://en.wikisource.org/wiki/The_ Mathematical_Principles_of_Natural_Philosophy_(1729) [Google Scholar]
- P. Delsarte, J. Goethals, J. Seidel: Spherical codes and designs, in Geometry and combinatorics, D.G. Corneil, R. Mathon (Eds.), Academic Press, 1991, pp. 68–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-189420-7.50013-X [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- F. Jacobsen, T. Roisin: The coherence of reverberant sound fields. Journal of the Acoustical Society of America 108 (2000) 204–210. https://doi.org/10.1121/1.429457 [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- R. Nicol: Restitution sonore spatialisée sur une zone étendue: application á la téléprésence. PhD dissertation, Université du Maine, 1999. Available at https://theses.hal.science/tel-01067541/document [Google Scholar]
- J. Daniel: Représentation de champs acoustiques, application á la transmission et á la reproduction de scénes sonores complexes dans un contexte multimédia. PhD dissertation, Université de Paris 6, 2001. Available at http://gyronymo.free.fr/audio3D/downloads/These-original-version.zip [Google Scholar]
- D. Ward, T. Abhayapala: Reproduction of a plane-wave sound field using an array of loudspeakers. IEEE Transactions on Speech and Audio Processing 9 (2001) 697–707. https://doi.org/10.1109/89.943347 [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- R.A. Kennedy, P. Sadeghi, T.D. Abhayapala, H.M. Jones: Intrinsic limits of dimensionality and richness in random multipath fields. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing 55 (2007) 2542–2556, 2007. https://doi.org/10.1109/TSP.2007.893738 [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- M.A. Poletti: Three-dimensional surround sound systems based on spherical harmonics. Journal of the Audio Engineering Society 53 (2005) 1004–1025. http://www.aes.org/e-lib/browse.cfm?elib=13396 [Google Scholar]
- J. Ahrens: Analytic methods of sound field synthesis. Springer, 2012. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-25743-8 [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- P. Grandjean, A. Berry, P.-A. Gauthier: Sound field reproduction by combination of circular and spherical higher-order ambisonics: part I – a new 2.5-D driving function for circular arrays. Journal of the Audio Engineering Society 69 (2021) 152–165. Available at http://www.aes.org/e-lib/browse.cfm?elib=21024 [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- P. Stitt, S. Bertet, M. van Walstijn: Off-centre localisation performance of ambisonics and hoa for large and small loudspeaker array radii. Acta Acustica united with Acustica 100 (2014) 937–944. https://doi.org/10.3813/AAA.918773 [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- M. Frank, F. Zotter: Exploring the perceptual sweet area in ambisonics, in 142nd AES Convention, Berlin, Germany, 20–23 May, 2017. http://www.aes.org/e-lib/browse.cfm?elib=18604 [Google Scholar]
- F. Zotter, M. Frank: Ambisonics. SpringerOpen, Cham, 2019. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-17207-7 [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- K. Merimaa, V. Pulkki: Spatial impulse response rendering I: analysis and synthesis. Journal of the Audio Engineering Society 53, (2005) 1115–1127. http://www.aes.org/e-lib/browse.cfm?elib=13401 [Google Scholar]
- J. Merimaa: Energetic sound field analysis of stereo and multichannel loudspeaker reproduction, in 123rd AES Convention, 5–8 October, New York, NY, 2007. http://www.aes.org/e-lib/browse.cfm?elib=14315 [Google Scholar]
- T.L. Curtright, Z. Cao, S. Huang, J.S. Sarmiento, S. Subedi, D.A. Tarrence, T.R. Thapaliya: Charge densities for conducting ellipsoids. European Journal of Physics 41 (2020) 035204. https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6404/ab806a [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- I.V. Lindell: Charge density on a conducting ellipsoid and an elliptic disk. American Journal of Physics 65 (1997) 1113–1114. https://doi.org/10.1119/1.18731 [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- W. Thomson: Reprint of Papers on Electricity and Magnetism, 2nd edn. MacMillan, London, 1884. Available at https://openlibrary.org/books/OL24349305M [Google Scholar]
- Y.V. Samukhina, N.E. Rusakova, P.A. Polyakov: Dependence of surface charge density on curvature of surface of conductive body with complicated shape. Journal of Electrostatics 125 (2023) 103844. Available at https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0304388623000530 [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- K. Bhattacharya: On the dependence of charge density on surface curvature of an isolated conductor. Physica Scripta 91 (2016) 035501. https://doi.org/10.1088/0031-8949/91/3/035501 [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- A.D. Alawneh, R.P. Kanwal: Singularity methods in mathematical physics. SIAM Review 19 (1977) 437–471. http://www.jstor.org/stable/2029614 [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- W. Hwang: A regularized boundary integral method in potential theory. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering 259 (2013) 123–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cma.2013.02.005 [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- D. Caratelli, J. Gielis, I. Tavkhelidze, P.E. Ricci: The dirichlet problem for the laplace equation in supershaped annuli. Boundary Value Problems 113 (2013) 1. https://doi.org/10.1186/1687-2770-2013-113 [Google Scholar]
- B. Makhdum, A. Nadim: Dynamics and equilibria of n point charges on a 2D ellipse or a 3D ellipsoid. Applied Mathematics 14 (2023) 4. https://doi.org/10.4236/am.2023.144015 [Google Scholar]
- D. P. Hardin, E. B. Saff: Discretizing manifolds via minimum energy points. Notices of the AMS 51 (2004) 1186–1194. https://www.ams.org/journals/notices/200410/fea-saff.pdf [Google Scholar]
- J. Fliege, U. Maier: The distribution of points on the sphere and corresponding cubature formulae. IMA Journal of Numerical Analysis 19 (1999) 317–334. https://doi.org/10.1093/imanum/19.2.317 [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- J. Korevaar, J. Meyers: Spherical faraday cage for the case of equal point charges and chebyshev-type quadrature on the sphere. Integral Transforms and Special Functions 1 (1993) 105–117. https://doi.org/10.1080/10652469308819013 [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- F. Fahy: Foundations of engineering acoustics. Elsevier Academic Press, San Diego, 2001. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-247665-5.50025-4 [Google Scholar]
- V. Pulkki: Spatial sound reproduction with directional audio coding. Journal of the Audio Engineering Society 55 (2007) 503–516. http://www.aes.org/e-lib/browse.cfm?elib=14170 [Google Scholar]
- J.J. Zwislocki, H.N. Jordan: On the relations of intensity JNDs to loudness and neural noise. Journal of the Acoustical Society of America 79 (1986) 772–780. https://doi.org/10.1121/1.393467 [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- T. Slade, A. Gascon, G. Comeau, D. Russell: Just noticeable differences in sound intensity of piano tones in non-musicians and experienced pianists. Psychology of Music 51 (2023) 924–937. https://doi.org/10.1177/03057356221126203 [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- A. Avni, B. Rafaely: Interaural cross correlation and spatial correlation in a sound field represented by spherical harmonics. in: Proceedings of 1st Ambisonics Symposium, Graz, Austria, 25–27 July, 2009. Available at https://iaem.at/ambisonics/symposium2009/proceedings/ambisym09-avnirafaely-iaccspatcorrsh.pdf [Google Scholar]
- J. Merimaa, V. Pulkki: Spatial impulse response rendering, in Proceedings of the DAFx, Naples, Italy, 5–8 October, 2004 [Google Scholar]
- A. Walther, C. Faller: Interaural correlation discrimination from diffuse field reference correlations. Journal of the Acoustical Society of America 133 (2013) 1496–1502. https://doi.org/10.1121/1.4790473 [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- W.M. Hartmann, Z.A. Constan: Interaural level differences and the level-meter model. Journal of the Acoustical Society of America 112 (2002) 1037–1045. https://doi.org/10.1121/1.1500759 [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- I. Pollack, W. Trittipoe: Binaural listening and interaural noise cross correlation. Journal of the Acoustical Society of America 31 (1959) 1250–1252. https://doi.org/10.1121/1.1907852 [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- B. Bernschütz: A spherical far field HRIR/HRTF compilation of the neumann KU 100, in 39th DAGA (AIA-DAGA), Merano, Italy, 18–21 March, 2013, pp. 592–595. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.3928297 [Google Scholar]
- A.H. Barr: Superquadrics and angle-preserving transformations. IEEE Computer Graphics and Applications 1 (1981) 11–23. https://doi.org/10.1109/MCG.1981.1673799 [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- J. Gielis: Superellipses to superformula: the impact of gielis transformations. Research Outreach 125 (2021). https://doi.org/10.13140/RG.2.2.26896.64005/2 [Google Scholar]
- J.A. Thorpe: Elementary topics in differential geometry. Springer, New York, 1979. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4612-6153-7 [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- W. Kühnel: Differentialgeometrie: Kurven-Flächen-Mannigfaltigkeiten, 6th edn. Springer Spektrum, Wiesbaden, 2013. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-658- 00615-0 [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- D. Caratelli, P. Ricci, J. Gielis: The robin problem for the laplace equation in a three-dimensional starlike domain. Applied Mathematics and Computation 218 (2011) 713–719, 2011, special Issue in Honour of Hari M. Srivastava on his 70th Birth Anniversary. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0096300311005261 [Google Scholar]
- D. Caratelli, P. Natalini, P.E. Ricci: Spherical harmonic solution of the robin problem for the laplace equation in supershaped shells, in Modeling in Mathematics, J. Gielis, P. E. Ricci, and I. Tavkhelidze (Eds.), Atlantis Press, Paris, 2017, pp. 17–30. https://doi.org/10.2991/978-94-6239-261-8_2 [Google Scholar]
- F. Zotter, S. Riedel, L. Gölles, M. Frank: Diffuse sound field synthesis, 2024. Available at https://arxiv.org/abs/2402.11330 [Google Scholar]
-
L. Gegenbauer: Über die Functionen
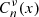 . Sitzungsberichte der Kaiserlichen Akademie der Wissenschaften. Mathematisch-Naturwissenschaftliche Classe 57 (1877) 8. Available at https://viewer.acdh.oeaw.ac.at/viewer/image/MN_2Abt_75_1877/904/LOG_0074/
[Google Scholar]
. Sitzungsberichte der Kaiserlichen Akademie der Wissenschaften. Mathematisch-Naturwissenschaftliche Classe 57 (1877) 8. Available at https://viewer.acdh.oeaw.ac.at/viewer/image/MN_2Abt_75_1877/904/LOG_0074/
[Google Scholar]
- F.W.J. Olver, A.B. Olde Daalhuis, D.W. Lozier, B.I. Schneider, R.F. Boisvert, C.W. Clark, B.R. Miller, B.V. Saunders, H.S. Cohl, M.A. McClain, Eds. NIST Digital Library of Mathematical Functions Release 1.1.9 of 2023-03-15. Available at https://dlmf.nist.gov/ [Google Scholar]
- J.J. Thomson: Xxiv. on the structure of the atom: an investigation of the stability and periods of oscillation of a number of corpuscles arranged at equal intervals around the circumference of a circle; with application of the results to the theory of atomic structure. Philosophical Magazine Series 39 (1904) 7. http://doi.org/10.1080/14786440409463107 [Google Scholar]
- L. Föppl: Stabile anordnungen von elektronen im atom. Journal für die Reine und die Angewandte Mathematik (1912). Available: https://www.digizeitschriften.de/id/243919689_0141 [Google Scholar]
- H. Harbrecht, W.L. Wendland, N. Zorii: Rapid solution of minimal riesz energy problems. Numerical Methods for Partial Differential Equations 32 (2016) 1535–1552. https://doi.org/10.1002/num.22060 [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- M. Gräf: Quadrature rules on manifolds. Available at https://www-user.tu-chemnitz.de/ potts/workgroup/graef/quadrature/ (accessed 2023/04/23) [Google Scholar]
- M. Gräf: Efficient algorithms for the computation of optimal quadrature points on riemannian manifolds. PhD dissertation, Chemnitz University of Technology, 2013. Available at https://www-user.tu-chemnitz.de/ potts/workgroup/graef/quadrature/papers/Gr13Diss.pdf [Google Scholar]
- M. Gräf and D. Potts: On the computation of spherical designs by a new optimization approach based on fast spherical fourier transforms. Numerische Mathematik 119 (2011) 699–724. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00211-011-0399-7 [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- F. Zotter, S. Riedel, L. Gölles, M. Frank: Source code for diffuse sound field synthesis, 2023. Available at https://git.iem.at/enimso/2023-diffuse-soundfield-synthesis-acta-jupyter-code [Google Scholar]
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


